Gender inclusion in the workplace: Going beyond diversity
Gender inclusion in the workplace is crucial for fostering a diverse and inclusive environment. It involves actively seeking to hire, promote, and engage women in leadership roles. This not only provides unique insights that can help a company grow but also creates a culture of respect and value for all employees, regardless of their gender.

Should we ban sports chat at work so that women don’t feel left out? This is a debate that sparkled a few days ago when Ann Francke, CEO at Chartered Management Institute, mentioned that talking about sports in the office could make female employees feel less included.
People were not happy with this comment – mainly because it’s based on the assumption that women in general don’t care about sports. Nevertheless, Francke’s statement might have been well-intentioned. She didn’t suggest banning sports talk completely; rather, it was an effort to shed light on behaviors that potentially sustain ‘bro culture’ at work. But even so, it raised some concerns as to whether we know how to improve (gender) inclusion in the workplace.
More than that: do we really know what inclusion means?
Contents
Diversity vs. Inclusion: why they’re not the same
It’s not by chance that when we talk about diverse teams and diverse workplaces, we, ultimately, mention diversity and inclusion (D&I). Sure, one could say they’re two sides of the same coin, but it’s important to make that distinction between ‘D’ and ‘I’. For example, if you’re hiring employees from underrepresented groups (e.g. people with disabilities, ethnic minorities, people from the LGBTQ+ community), you’re doing a great job in boosting diversity in your company.
But that’s not enough.
Think about it: After being hired, do these people feel like they belong? Are they confident and comfortable bringing their true selves to work or do they feel the need to hide their unique traits and points of view?
That’s where inclusion in the workplace matters. Simply raising the number of people from underrepresented groups that you employ – and ticking off those boxes – doesn’t guarantee that you’ve built a work environment of equal opportunities.
Back to the gender inclusion in the workplace discussion – if, for example, your sales team have quotas that require travelling, do you make adjustments to accommodate soon-to-be or new mothers? Another example could be the language used in corporate documents or during meetings – is it gender-inclusive or does it make some people in the room feel that they don’t belong there?
Gender discrimination in the workplace takes many forms
It’s not just about a pay gender gap. It’s not just offensive, sexist comments during meetings. It’s not just promotions for like-minded ‘bros’. It’s all of that and many more behaviors and stereotypes that poison the workplace culture.
TrustRadius recently published the 2020 Women in Tech Report in which men, women and non-binary respondents share their perspectives around gender dynamics in the workplace. Findings show that women are indeed feeling left out at work, whether it’s because they’re being paid less than their peer (or even less experienced) male colleagues or due to the overall office culture that favors men.
Here are some examples of what they had to say:


Lately, changes in law and global movements, like #MeToo, encourage women and other people from underrepresented groups to speak up when they experience inequality at work. One recent example is the story of Riot Games, the video game developer company behind popular games including “League of Legends”, where current and former employees accused the company for sexism and harassment. In the end, Riot Games agreed to pay $10 million as part of a settlement over alleged gender discrimination.
Similar stories on the lack of true inclusion in the workplace are all over the news. In 2018, Spotify was sued for equal pay violation and, a few months later, Oracle was also sued. But this is not limited to tech companies. Former Nike employees have filed lawsuits against alleged pay discrimination, Walmart has faced gender bias legal issues on more than one occasion, and Disney was hit with a lawsuit in early 2019.
The list continues to grow with lawsuits involving WeWork, firefighters, the US Women’s National Team, and others. That’s proof that we’re not talking about one-off incidents. It’s also proof (and a good sign) that employees do feel comfortable enough to file complaints. But you of course don’t want to be in the employer’s position in the first place. Not only is it expensive regardless of whether you’re found liable or not, it’s also debilitating to your employer brand and overall reputation as a company especially if it goes public. So, you’ll want to get ahead of it before anything happens. Think about what you can do before reaching this stage.
Inclusion requires a reality check
Let’s face facts: diversity is at first glance more easily measurable. You can track how many people from underrepresented groups you attract, hire and promote at your company. You can monitor how these numbers change over time, how they differ from department to department and if they’ve been positively impacted by any proactive diversity-inspired initiative you take.
Inclusion in the workplace, on the other hand, has less tangible metrics. You could track, analyze and correct any pay gender gaps you find – that part’s easy. You could enforce anti-harassment policies – that’s not hard to track either.
But how do you identify and address those less obvious sexist behaviors? Based on the TrustRadius report, 71% of women have worked at a tech company where bro culture was pervasive. That’s not a number to ignore. It might be now a good time to check your own company culture and try to discover in which ways you support – or don’t support – women in your workplace.
“Even companies that sell tampons are run by men”
This is the title of a not-so-old article from The Huffington Post that explored the impact of having men be responsible for feminine products. And while this particular situation has now been rectified to a degree, the story raises a good thinking point relevant to the workplace, in general: can we let a privileged group (men, in this case) decide what’s best for the least privileged group (women)? Or, even deeper, because stereotypes are largely infused in our way of thinking, can we recognize our unconscious biases?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XjJQBjWYDTs
When you want to boost D&I, the #1 step is to raise your awareness. In other words, to realize that if you don’t have diverse teams, you’re not building products or you’re not offering services that appeal to a broad audience. You’re missing out on opportunities to solve problems and to grow your business.
Taking this story to another level: it’s often argued that tampons would have been rendered obsolete a long time ago if men had periods. Of course, the business gains that are associated with diverse teams go beyond companies that sell feminine products.
And that brings us to step #2: perception. You now realize that you need diversity, but how diverse your company is? You’ll get that information if you look internally at how your teams are built, how you’re making strategic decisions and whether your workplace provides equal opportunities to all employees.
If you find that you’re not as diverse as you could be, your step #3 is decision: the decision to change internally so you increase diversity.
And that goes hand in hand with step #4: analysis. You shouldn’t look at the numbers only at a high level. For example, if you currently employ 10% female employees and decide to increase that number to 40-50%, it doesn’t mean that you’ll solve the issue. It’s not enough to just hire those women; you need to give them a seat at the table where decisions are being made.
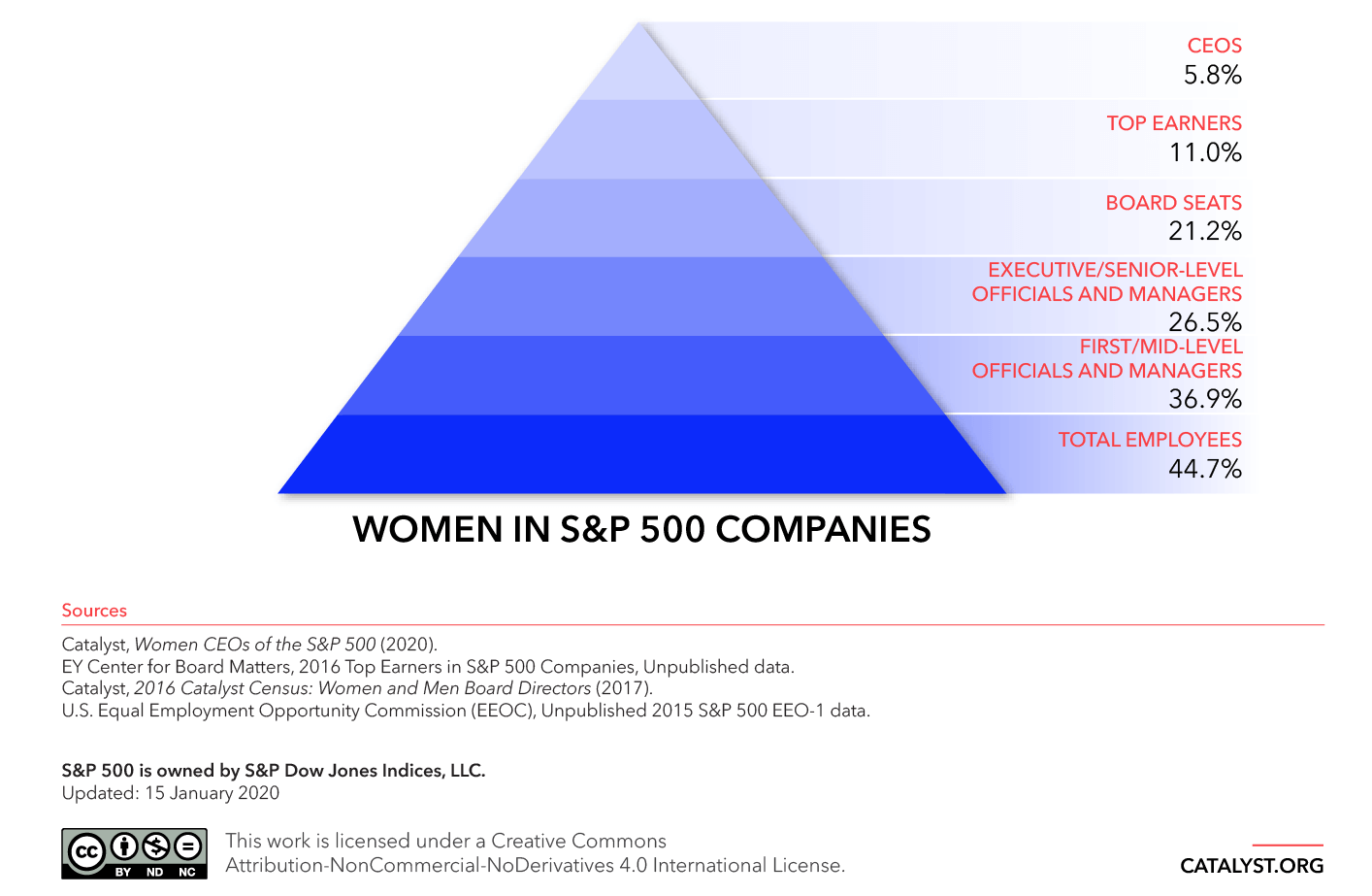
The following graph shows that while S&P 500 companies have almost 50-50 balance in male and female employees, the female representation at the more senior levels is significantly lower. When that’s the case, can we really talk about an equal workforce?
That’s when you can move on to step #5: action towards inclusion in the workplace. By default, ‘bros’ cannot recognize and define what bro culture is. Neither can they fix it. To use a simplified metaphor, a fish doesn’t know it’s in water.
Likewise, you can’t decide if your female colleague is feeling left out at work. She’s the one who knows what sexism, bullying or discrimination in the workplace looks and feels like, because she’s the one experiencing it. But the onus is on you as an employer to build a culture where she feels strong enough to raise that voice.
Perhaps you think that your company culture is inclusive. But the only way to know for sure is by going to the source: ask those who are usually affected by discrimination. Perhaps you assume that avoiding a discussion helps a group of people don’t feel excluded. But that’s not the same as actively including those people in the discussion.
Now, if it was you making the decision, would you choose to ban sports talk at work?
Frequently asked questions
- What is the importance of gender inclusion in the workplace?
- Gender inclusion is crucial in the workplace as it provides unique insights from women that can help a company grow. It fosters a diverse and inclusive environment that respects and values the contributions of all employees, regardless of their gender.
- What is gender diversity in the workplace?
- Gender diversity in the workplace refers to the active efforts made by employers to hire, promote, and engage women in leadership roles within the organization. It's about ensuring a balanced representation of genders across all levels and roles.
- What is gender-inclusive leadership?
- Gender-inclusive leadership means that leaders are committed to promoting equal opportunities. They recognize the challenges women face on their path towards leadership and actively support them with tangible ways of assistance, fostering a culture of inclusivity.
- How can we ensure gender inclusion in the workplace?
- Ensuring gender inclusion in the workplace involves raising awareness, changing perceptions, making strategic decisions, and providing equal opportunities to all employees. It's about actively including everyone in discussions and decision-making processes.
- What are the challenges of achieving gender inclusion in the workplace?
- Challenges to achieving gender inclusion include unconscious biases, bro culture, and a lack of representation in leadership roles. Addressing these issues requires a commitment to change and the implementation of policies that promote gender equality.




